Since this is a comprehensive topic, I've broken it into two articles. This article will focus on identifying the required skills for each role within the team. The other article will delve into career paths, why they need to be fixed, and how I categorize career paths into three tracks.
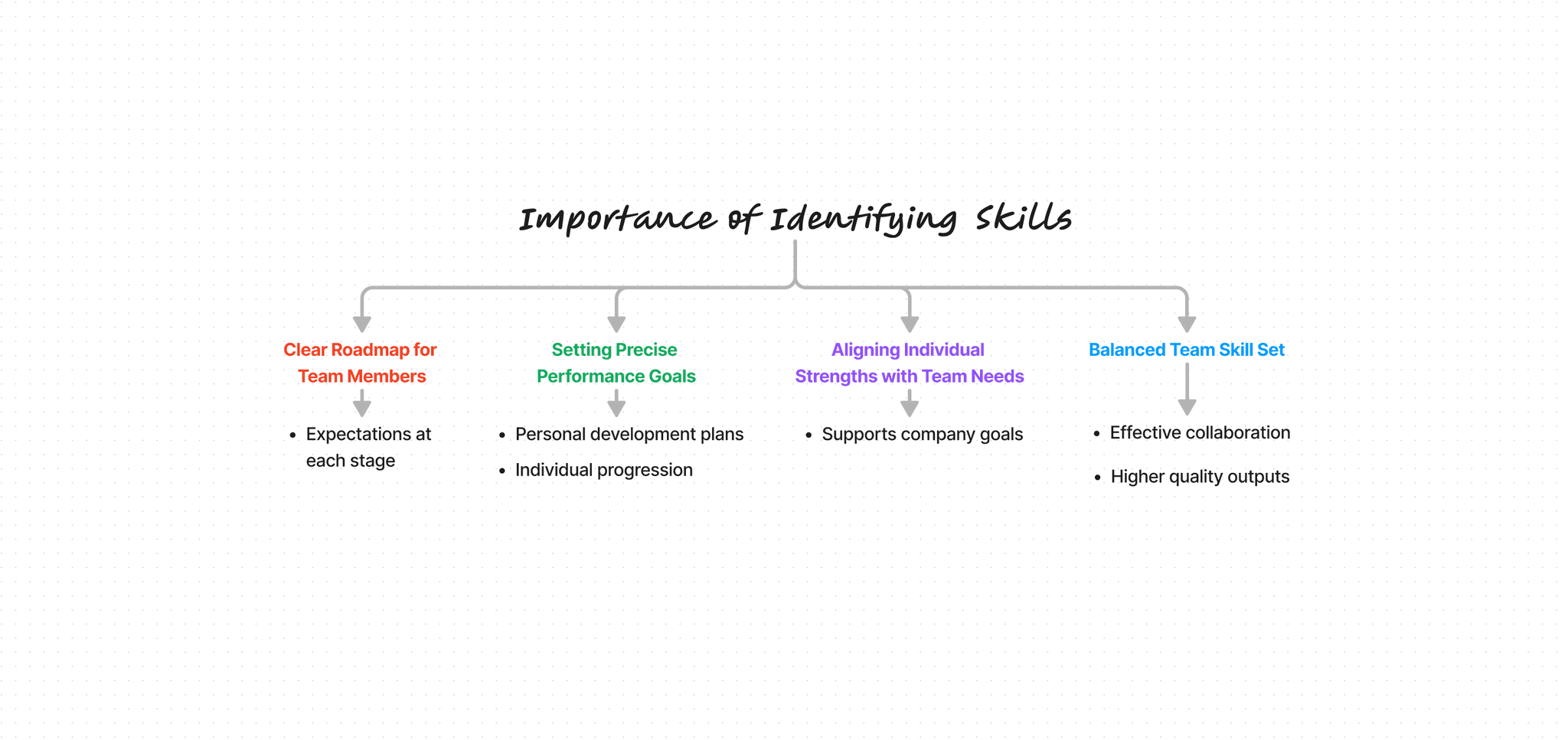
Why Identifying Skills Is Important
Identifying essential skills for each role is critical for several reasons. It provides a clear roadmap for team members, showing them what is expected at each stage of their career. This clarity helps in setting precise performance goals and personal development plans, making it easier for individuals to progress. Moreover, it ensures that the team possesses a balanced skill set, enabling more effective collaboration and higher quality outputs. Clearleft also emphasizes the importance of skill identification, noting that it aids in aligning individual strengths with team needs and overall company goals.
Inspiration from Clearleft
Clearleft's professional development framework served as a significant source of inspiration. Their comprehensive approach to defining roles and skills in design and UX provided a valuable blueprint. By analyzing Clearleft's framework, I gained insights into structuring roles, identifying core competencies, and creating a progression path that supports both individual and team growth.
Defining a Role
Following Clearleft's example, I began by drafting an initial framework that defined each role within the team, including associated career paths. This draft provided a foundation for further discussion and refinement with my team leads. By outlining expected competencies, and potential career trajectories, we were able to collaboratively refine these roles to ensure they met both individual and organizational needs.
Foundation Skills
Foundation skills are essential attributes that every team member must possess, regardless of their specific role. These include communication, problem-solving, empathy, and strategic thinking. These skills ensure that team members can collaborate effectively, understand and solve user problems, and contribute to strategic goals. Regular assessment of these foundational skills helps maintain a high baseline of competency across the team.
Specialist Skills
In addition to foundational skills, specialist skills are critical for roles in design, UX, research, and leadership. These skills vary depending on the role and are tailored to meet the specific needs of each domain. For instance, a UX specialist might need deep expertise in user research and customer journey map, while a design specialist focuses on visual design and branding. Not all skills are relevant to every role, but identifying them ensures that team members can develop expertise in their chosen field.
Skills in 5 Levels
To further clarify career progression, I categorized knowledge and skills into five levels: Beginner, Novice, Intermediate, Expert, and Master. Each level corresponds to increasing degrees of competency and responsibility. This structured approach helps team members identify where they currently stand and what they need to achieve to advance to the next level. It also provides a clear framework for performance evaluations and goal setting.
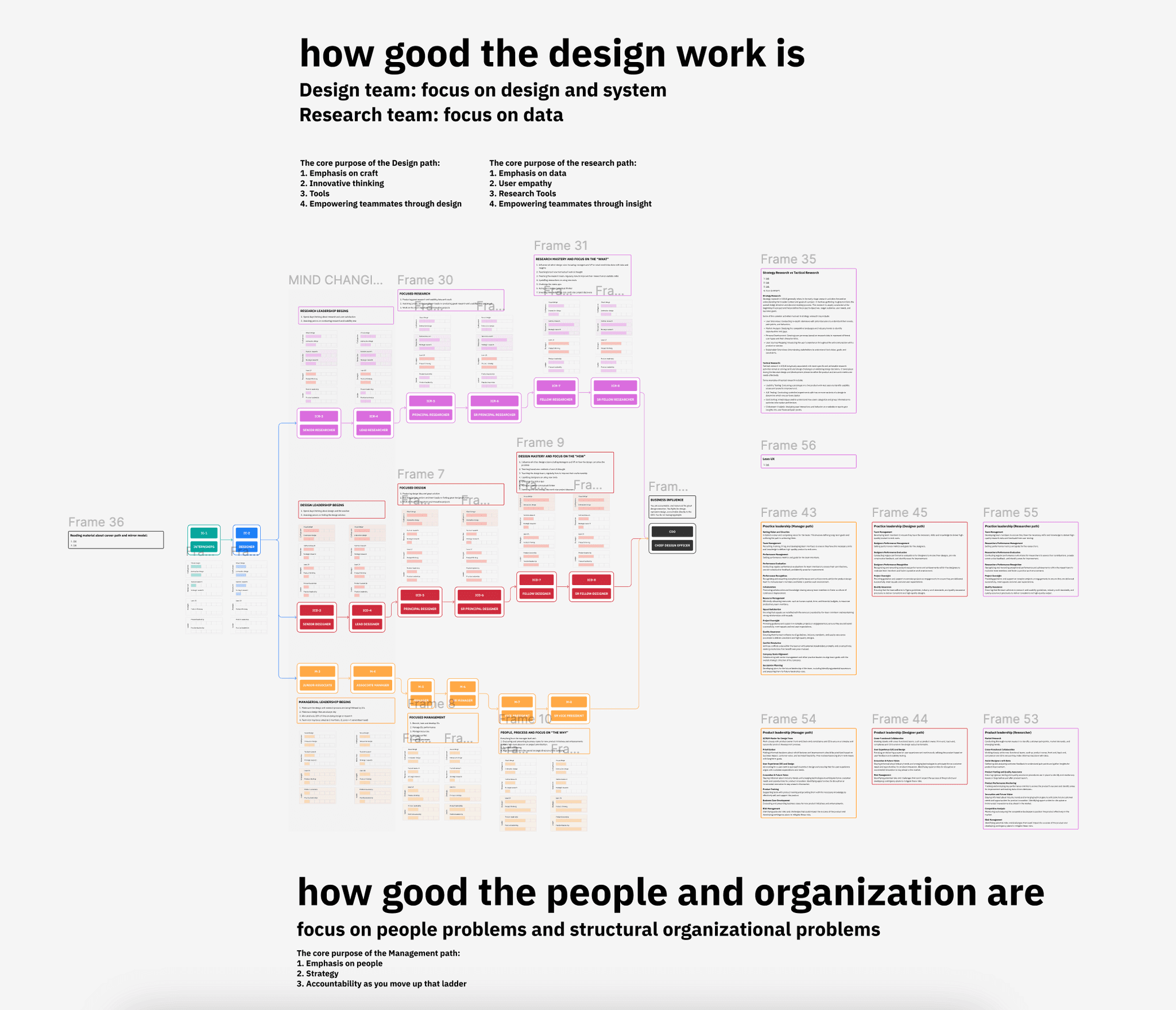
Final Approved Career Paths
After extensive research and careful design, we have finalized the career paths for each profession within the UI/UX team. These paths clearly outline the progression, roles, and skills required for each track, ensuring that every team member has a clear and achievable path for career advancement.
Below, you will find the career paths for Research, UX, and Design professions, each tailored to meet the unique demands and strengths of the respective fields.